 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Nicola Barts
Photo: Nicola Barts
ABOUT INSULATION The thermal barrier of a home should consist of a continuous layer of insulation on all sides—including the lowest floor, the exterior walls, and the ceiling or roof. Doubling the thickness of insulation will double the insulation's R-value, cutting heat loss in half.

Here's how: Measure the wall, ceiling, and floor area of your metal shed. Remove internal wall sheathing, if necessary. Using closed-cell spray...
Read More »
Here is the list f selected hot business opportunities with good profit potential: Start a Blog. You can choose to start a blog of your own on a...
Read More »ABOUT INSULATION Thicker is better In cold weather, a puffy parka holds in your body heat. Insulation does the same thing for a house. The thicker the insulation, the better it works to reduce heat flow from the inside of a home to the outside during winter, and from outside to inside during summer. The thermal barrier of a home should consist of a continuous layer of insulation on all sides—including the lowest floor, the exterior walls, and the ceiling or roof. Doubling the thickness of insulation will double the insulation’s R-value, cutting heat loss in half. Each time the insulation layer is doubled in thickness, this rule applies. The energy saved per year by doubling insulation from R-10 to R-20, however, will be considerably more than the energy saved by doubling insulation from R-20 to R-40, because of the law of diminishing returns. In some cases, like an attic, it’s worth piling on more insulation because there is plenty of room. It’s much more expensive to add that much insulation to exterior walls. It takes more than just insulation to slow heat Stopping air leaks is just as important as — maybe more important than — adding insulation. Unless builders prevent air from leaking through walls and ceilings, insulation alone won’t do much good. Not only are drafts uncomfortable, but air moving through insulated cavities can cut the efficiency of the insulation by as much as 50%. Some insulation types make good air barriers, and some don’t. In all cases, it’s best to keep the insulation tight to the air barrier. THERMAL BRIDGING IS CONDUCTION IN ACTION When there is no insulation in a roof or wall, the framing is the most insulated part of the assembly. It has the highest R-value. Softwood lumber has an R-value of 1.25 per inch, so a 2×6 stud has an R-value of almost 7. As soon as you put insulation between the studs or rafters above R-7, however, the framing becomes the weak thermal link. If the framing cavities are filled with closed-cell spray foam insulation, the insulation has an R-value of about 36. At that point, the studs or rafters become a glaring weakness in the design. Building scientists call this phenomenon “thermal bridging” because the studs or rafters bridge the space between inside and outside the thermal envelope. If you look for it, thermal bridging can sometimes be seen from either inside or outside. Inside, it can cause a problem called ghosting, or cold stripes behind the drywall during winter. These cold stripes can encourage condensation that leads to the accumulation of dust particles on the drywall; eventually, visible vertical stripes may form. Outside, you can see the effect of thermal bridging in snow-melt patterns on roofs and drying patterns on walls. A continuous layer of rigid foam installed on the inside or outside of a wall or roof drastically reduces thermal bridging through the framing. R-VALUE MEASURES HOW WELL INSULATION WORKS Heat flows from hot to cold; it can’t be stopped, but it can be slowed If we measure the rate at which heat flows through a building material or building assembly—for example, a wall or a roof—we can calculate a number (the R-value) to indicate its insulating ability. The higher a material’s R-value, the better the material is at resisting heat flow through conduction, convection, and radiation (outlined above). Insulation manufacturers report R-values determined by tests following ASTM standards (for example, ASTM C518). Common insulation types and their R-values Residential insulation materials have R-values that range from about 3 to 7 per inch. The amount of insulation installed in any given building assembly depends on the climate, the part of the house being insulated, the project budget, and local code requirements. Batts and blankets: R-3.1 to R-4.1 per in.

So to charge one battery of 400 AH, the panel rating needed is 100*12 = 1200 Watts. For 3 batteries, you'll require 3600 Watts rating PV solar...
Read More »
I used 4 meterials (cups) polystyrene, paper, porcelain and metal. Polystyrene was the best insulator followed by paper, porcelainand then metal. I...
Read More »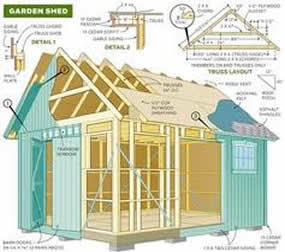
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
Put the rebar on top of a raised non-metallic platform, such as wooden pallets. Both the ground and concrete areas absorb moisture and can lead to...
Read More »
Does Spray Foam Keep Out Mice, Rodents and Pests? The quick answer to this question is yes, spray foam will work to keep out mice and other pests....
Read More »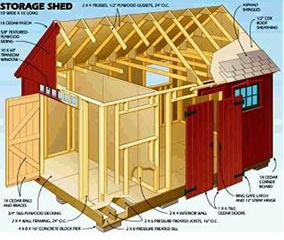
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
Excess water outside the shed must have an escape route away from the building. The foundation should contain a damp-proof membrane which should be...
Read More »

20 feet Ramp Calculations According to ADA standard, you'll need a ramp of 1 foot per inch of rise height. For example, if your rise is 20 inches,...
Read More »