 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Pixabay
Photo: Pixabay
Do you need a 25mm air gap under the membrane? Although this is standard practice, it is not a requirement. The important thing is that you should not push the drape in the breather membrane (which allows any water getting through the tiles to channel down to the gutter) out.

A good paint job provides both decoration and protection. Unless you have an early barn with rough vertical board siding that was never meant to be...
Read More »
A 10”x12” or 8”x12” shed is all you need for de-cluttering the push mower, flower pots, tools, and lawn supplies easily and effectively. Indulge in...
Read More »
In my experience, I've found more ants nesting within thick layers of large stone gravel.
Read More »
Log cabins or wooden garages are considered as 'temporary structures' and as a result don't generally need planning approval.
Read More »Materials such as rigid foam insulation, reinforced plastics, aluminum, and stainless steel are relatively resistant to water vapor diffusion. These types of vapor retarders are usually mechanically fastened and sealed at the joints.
In most U.S. climates, vapor barriers, or -- more accurately -- vapor diffusion retarders (vapor retarders), should be part of a moisture control strategy for a home. A vapor retarder is a material that reduces the rate at which water vapor can move through a material. The older term "vapor barrier" is still used even though "vapor retarder" is more accurate. The ability of a material to retard the diffusion of water vapor is measured in units known as "perms" or permeability. The International Residential Code describes three classes of water vapor retarders:

Here's six techniques to create heat in the absence of electricity or fire: Insulate your body. Insulate your environment. Keep moving. Light a...
Read More »
Pallets, lumber, and other cut and dried scrap wood are indeed good to burn (as long as you are completely sure they were not treated with any...
Read More »

A bit of insulation under the concrete layer slows the penetration of cold down into the earth. This can help you prevent frost heaving because the...
Read More »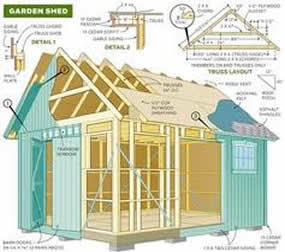
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
To raise the back of the building: Place the 2-foot level in the location that needs to be leveled. Raise the building until the bubble is directly...
Read More »