 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Lukas Rychvalsky
Photo: Lukas Rychvalsky
152 feet As an example, for a 120-volt circuit, you can run up to 50 feet of 14 AWG cable without exceeding 3 percent voltage drop. ... For 240-volt circuits: 14 AWG 100 feet 12 AWG 120 feet 10 AWG 128 feet 8 AWG 152 feet 6 AWG 188 feet

6 to 18 hours For most concrete work, cutting should take place within the first 6 to 18 hours and never beyond 24 hours. Smaller early-entry saws...
Read More »
carpentry. noun. the activity of making things from wood, or repairing things that are made of wood.
Read More »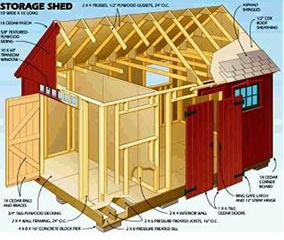
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »Underground wire for a residential circuit usually is installed with underground feeder (UF) cable, which is rated for outdoor use and direct burial. Such an installation is typical when running a circuit to an outdoor location, such as a garage, shed or other outbuilding, or to a yard light or water feature. Sizing the wires, or conductors, for an underground cable is no different than sizing for other household circuits and is typically based on the total load, or electrical demand, of the devices on the circuit. However, if the cable run is long, as underground runs often are, you may need to increase the wire size to account for voltage drop—a loss of voltage in the circuit caused by the natural resistance in the wires. Voltage drop occurs in any wire run, but it is rarely a problem with indoor wiring, where the distance from the circuit breaker panel to the end of the circuit is usually relatively short. Outdoor circuits, however, are often quite long and the voltage drop can be significant.

ANSWER: The ivy will belong to the neighbour as its roots appear to come from the neighbouring property. If the end-terrace wall is structurally...
Read More »
Fencing increases the value of your home by a fraction of the price of the fencing. If you have a $10,000 fence installed, your home value is...
Read More »
Since voltage drop is caused by the resistance of conductors, the more conductors you have, the greater the voltage drop. When it comes to underground wire, the longer the wire, the greater the voltage drop. Wire size is another factor: Smaller-diameter wires have more resistance than larger-diameter wires. Copper wire has lower resistance than aluminum wire, but chances are good that you'll be using copper in any case. These days, the only aluminum used in most new residential projects is in the service entrance cables from the utility, although you may see aluminum show up on voltage drop tables.

1. Price. Although Quikrete is more expensive than traditional concrete, it is much cheaper to install in comparison. In fact, the average...
Read More »
sand Good holding The best surfaces are sand or mud, which allow the anchor to dig in deeply. Rock and weed or shingle will provide a less secure...
Read More »
The optimal temperature range is for conventional mini split heat pump operation is over 25-30 degrees Fahrenheit. As the temperature goes down to...
Read More »
Quick summary. As long as your shed is under 2.5m tall at the eaves, situated in your back garden away from property boundaries, and intended for a...
Read More »