 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Andrea Piacquadio
Photo: Andrea Piacquadio
For most people, exterior plywood in a build will be sufficiently offgassed by the time the building is complete. If you are extremely sensitive you should test out plywood when new, after a few weeks and after 2-3 months of airing. You should also compare that to OSB, to see which is better for your health.

Boxabl are made from steel, concrete and EPS foam. These are building materials that don't degrade and will last a lifetime. The walls, floor and...
Read More »
If you retire with $500k in assets, the 4% rule says that you should be able to withdraw $20,000 per year for a 30-year (or longer) retirement. So,...
Read More »
A Guide to Choosing Pressed, Engineered and Laminated Wood Products and their Formaldehyde and VOC Levels This post will cover pressed wood and laminated wood (engineered wood) products used in construction and in household items like furniture and doors. We will look at which adhesives are used and what chemicals they offgas. Formaldehyde levels will be noted, as they vary between engineered wood types. But not all engineer wood is pressed together with formaldehyde.

2-grade 2×6 joists can span up to 10 feet 9 inches from beam to beam when spaced the standard 16 inches apart with a maximum live load of 30 inches...
Read More »
A furniture flipping business can be incredibly profitable, and it's a great way for you to earn some extra cash on the side — or even replace your...
Read More »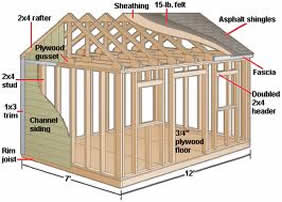
It is made of softwood, usually fir, spruce and/or pin). In Canada, Douglas Fir Plywood (DFP) (can have up to 21 other species of woods in the inner plies), and Canadian softwood plywood (CSP) may have balsam poplar, trembling aspen, and cottonwood.

Pavers are held in place by gravity and each other. They are not cemented together, so you cannot anchor something like a gazebo, pool cover or...
Read More »
As a product, spray foam insulation does not attract mold. And unlike wood or metal, spray foam does not rot, rust or deteriorate. This means that...
Read More »

Converting your shed into a living space can run from $1,500 up to $30,000, depending on the following factors: Material cost. Labor. Cost of...
Read More »
Making your house more efficient, adding square footage, upgrading the kitchen or bath and installing smart-home technology can help increase its...
Read More »

Here are the steps you should follow: Pour the first layer; these are huge stones. Evenly distribute it over the area. Compact it using a compactor...
Read More »

Plastic bags are commonly used to cover plants because they provide protection from pests, disease, excessive moisture, and even frost. When a...
Read More »