 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: t4hlil
Photo: t4hlil
Thicker is better The thermal barrier of a home should consist of a continuous layer of insulation on all sides—including the lowest floor, the exterior walls, and the ceiling or roof. Doubling the thickness of insulation will double the insulation's R-value, cutting heat loss in half.

Can a queen-size bed fit in a 5x5 storage unit? Normally, queen mattresses are 60 inches wide by around 80 inches long. Based on these dimensions,...
Read More »
The 2-out-of-five-year rule states that you must have both owned and lived in your home for a minimum of two out of the last five years before the...
Read More »
ABOUT INSULATION Thicker is better In cold weather, a puffy parka holds in your body heat. Insulation does the same thing for a house. The thicker the insulation, the better it works to reduce heat flow from the inside of a home to the outside during winter, and from outside to inside during summer. The thermal barrier of a home should consist of a continuous layer of insulation on all sides—including the lowest floor, the exterior walls, and the ceiling or roof. Doubling the thickness of insulation will double the insulation’s R-value, cutting heat loss in half. Each time the insulation layer is doubled in thickness, this rule applies. The energy saved per year by doubling insulation from R-10 to R-20, however, will be considerably more than the energy saved by doubling insulation from R-20 to R-40, because of the law of diminishing returns. In some cases, like an attic, it’s worth piling on more insulation because there is plenty of room. It’s much more expensive to add that much insulation to exterior walls. It takes more than just insulation to slow heat Stopping air leaks is just as important as — maybe more important than — adding insulation. Unless builders prevent air from leaking through walls and ceilings, insulation alone won’t do much good. Not only are drafts uncomfortable, but air moving through insulated cavities can cut the efficiency of the insulation by as much as 50%. Some insulation types make good air barriers, and some don’t. In all cases, it’s best to keep the insulation tight to the air barrier. THERMAL BRIDGING IS CONDUCTION IN ACTION When there is no insulation in a roof or wall, the framing is the most insulated part of the assembly. It has the highest R-value. Softwood lumber has an R-value of 1.25 per inch, so a 2×6 stud has an R-value of almost 7. As soon as you put insulation between the studs or rafters above R-7, however, the framing becomes the weak thermal link. If the framing cavities are filled with closed-cell spray foam insulation, the insulation has an R-value of about 36. At that point, the studs or rafters become a glaring weakness in the design. Building scientists call this phenomenon “thermal bridging” because the studs or rafters bridge the space between inside and outside the thermal envelope. If you look for it, thermal bridging can sometimes be seen from either inside or outside. Inside, it can cause a problem called ghosting, or cold stripes behind the drywall during winter. These cold stripes can encourage condensation that leads to the accumulation of dust particles on the drywall; eventually, visible vertical stripes may form. Outside, you can see the effect of thermal bridging in snow-melt patterns on roofs and drying patterns on walls. A continuous layer of rigid foam installed on the inside or outside of a wall or roof drastically reduces thermal bridging through the framing. R-VALUE MEASURES HOW WELL INSULATION WORKS Heat flows from hot to cold; it can’t be stopped, but it can be slowed If we measure the rate at which heat flows through a building material or building assembly—for example, a wall or a roof—we can calculate a number (the R-value) to indicate its insulating ability. The higher a material’s R-value, the better the material is at resisting heat flow through conduction, convection, and radiation (outlined above). Insulation manufacturers report R-values determined by tests following ASTM standards (for example, ASTM C518). Common insulation types and their R-values Residential insulation materials have R-values that range from about 3 to 7 per inch. The amount of insulation installed in any given building assembly depends on the climate, the part of the house being insulated, the project budget, and local code requirements. Batts and blankets: R-3.1 to R-4.1 per in.

From 2021, the use of disposable plastic, including bubble wrap, will be banned. What will replace the bubbles? Jan 6, 2020
Read More »
The cost to build a deck that is 10×10 in size is approx $2,000, $6,500 to build a 14×20 foot deck, and $8,800 to build a 20×20 foot deck. A deck...
Read More »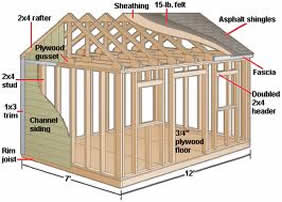

A general rule of thumb is that facing the opening toward the south is a good place to start. Because most of the prevailing winds come from the...
Read More »
Natural ways to get rid of mold Vinegar. Vinegar is an affordable, natural solution to getting rid of mold. ... Baking soda. ... Tea tree oil. ......
Read More »

Your neighbour doesn't have to change a wall or fence just because you want them to, for example making it higher for privacy. You can't make...
Read More »

What Are the Important Kitchen Updates that Add Home Value? Cabinet Refacing and Refinishing. ... Update Your Kitchen Countertops. ... Modern Tile...
Read More »