 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Anna Tarazevich
Photo: Anna Tarazevich
House mice are eaten by a wide variety of small predators throughout the world, including cats, foxes, weasels, ferrets, mongooses, large lizards, snakes, hawks, falcons, and owls. House mice try to avoid predation by keeping out of the open and by being fast.

DON'T plug high-capacity appliances into a power strip. Refrigerators. Washing machines and dryers. Sump pumps. Space heaters. Portable air...
Read More »
Plywood has a lot of properties that make it great for lining the interior of a shed. For its thickness, plywood is very strong, making it great...
Read More »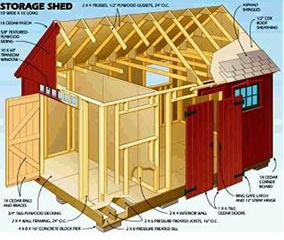
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
Permission isn't usually required for a garage conversion, provided the work is internal and doesn't involve enlarging the building. However, you...
Read More »
Boric acid (borate) is one of the most effective fungicides for use in treating wood rot. It can be applied to wood during construction to prevent...
Read More »

The average price for a basic 12×20 shed that is painted ranges between $3, 970 – $4,650. Additional special customizations may increase the final...
Read More »
If your shed has windows you don't mind obstructing, you can opt for a window air conditioner. It is designed to cool a single space and can make a...
Read More »

Rafter size for 16 foot span As per general rules and guidelines, rafter made of pine wood, for a 16 foot span, size of rafter should be 2″×8″ in...
Read More »
A greenhouse is a storage place for plants to grow, keeping them protected from the outside weather conditions. A potting shed can also store...
Read More »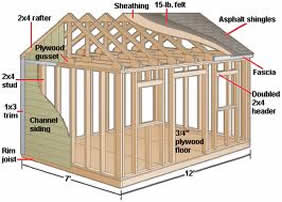

According to Opendoor's data, adding a full bathroom can increase the median home value by 5.7% on average, which is a dollar increase of about...
Read More »
Cleaning Solutions We find either a bucket of warm water containing light detergent or warm water inclusive of a splash of washing up liquid plus a...
Read More »