 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Quang Nguyen Vinh
Photo: Quang Nguyen Vinh
Anchor types Admiralty anchor. CQR anchor. Bruce anchor. Danforth anchor. Grapnel anchor.

100-square-foot Generally, a cubic yard of gravel provides enough material to cover a 100-square-foot area with 3 inches of gravel. Jul 2, 2022
Read More »
Concrete foundations for a summer house? The usual advice for concrete is to put a 7-10 cm layer of concrete above 7 cm of compacted hardcore....
Read More »

Boltless shelving is a form of industrial storage configured without nuts or bolts. This type of shelving is designed for easy assembly. You can...
Read More »
Key Takeaways The rule states that you should spend up to 50% of your after-tax income on needs and obligations that you must-have or must-do. The...
Read More »
It simply meant abstaining from eating the flesh of warm-blooded animals—since the thinking goes, Jesus was a warm-blooded animal. Fish, though,...
Read More »
If Your Time is short. The best ways to stay warm during a power outage are to wear layers, stay in a confined space, use blankets and battery-...
Read More »
between $100 and $250 per linear foot Wheelchair ramps made of wood typically cost between $100 and $250 per linear foot to install. Installing a...
Read More »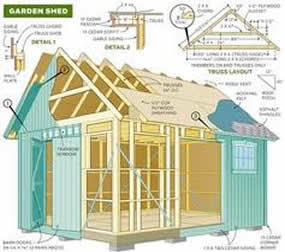
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
The shoebox design is a classic format that some say produces the best acoustics, with nine out of the world's top 10 concert halls having this...
Read More »