 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: cottonbro studio
Photo: cottonbro studio
Mold is unable to digest inorganic materials (such as concrete, glass, and metal), but it can digest and grow on the dirt, dust, and organic residue that accumulates on them.

Most hotels use peroxide-based laundry detergents to keep their sheets and towels bright. While these compounds are extremely successful at...
Read More »
Planning permission to build and Access Requests Even if your neighbour has planning permission to build a structure, if any part of it has to be...
Read More »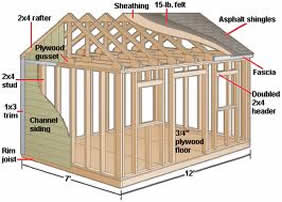

90-mile-per-hour If you don't, the structure could be weakened and it could possibly collapse. Code buildings are designed to be able to stand up...
Read More »
Speaking to The Sun, the Chartered Town Planner of 14 years' experience explained: "An outbuilding can be built using 'permitted development...
Read More »

There are so many different ways to use sheds now, and an 8×12 shed is the perfect size for a starter wooden shed: not so large that it will take...
Read More »
Can Metal Roofing Be Installed Directly to Plywood? Metal roofing should not be installed directly over the top of bare plywood. You do not have to...
Read More »Trichoderma: Trichoderma is less common than the first three types of mold. Its infrequency is in part because it requires more moisture than the others. This mold grows on untreated lumber, pine wood and boards, decaying wood, and textiles. No matter what mold is on your exterior surfaces, it’s important to remove it swiftly and thoroughly. This will reduce damage to the materials and structures that mold grows on. Outdoor mold can be easily taken care of with Wet & Forget Outdoor Concentrate – an easy, gentle, and bleach-free outdoor cleaner that is safe for virtually any exterior surface.

If you already have a shed that is not being used very much, you could save some money and simply convert your old shed into a beautiful art...
Read More »
Pressure-treated plywood is one of the best options for shed flooring. Pressure-treated plywood is resistant to wood rot, insects, and water. It is...
Read More »
How Do You Stop Dampness In A Shed? Insulate. Insulation not only makes your shed more energy efficient by reducing heat gain and loss, it also...
Read More »

6 Tips to Season Firewood Quickly Know the What Type of Wood You're Using. The type of wood you use matters. ... Prepare During the Right Time of...
Read More »