 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Mikhail Nilov
Photo: Mikhail Nilov
Coremakers who work by hand may be known as bench coremakers or floor coremakers, depending on the size of the cores that they make. More and more cores are being made by machine. Operators of these machines are known as machine coremakers.

Gas Boiler Alternative Electric Radiators. ... Electric Water Heaters. ... Heat Pumps. ... Hybrid heating system. ... Solar Thermal Panels. ......
Read More »
For effective openings not greater than one-half inch, a minimum airgap of one inch is required. Therefore, all airgaps must be at least one inch...
Read More »
Foundry Industry Job Descriptions, Careers in the Foundry Industry, Salary, Employment Definition and Nature of the Industry, Education and Training Requirements, Getting the Job Pots and pans, bathtubs, and automobile engine blocks are among the many kinds of products made by casting metals in foundries. There are several methods of shaping metals. The method used depends on the kind of metal and the intended use of the finished product. Casting is a relatively simple and inexpensive method that can produce intricate shapes and that can be easily adapted to the techniques of mass production. Metal is cast by heating it until it is a liquid and then pouring it into a specially prepared mold. As the metal cools, it becomes solid and takes on the shape of the mold. Many workers in this industry are employed by independent foundries that make and sell castings to other manufacturing companies. Manufacturing companies that make finished products also employ foundry workers. For example, automobile manufacturers have their own foundries that make engine blocks, crankshafts, and other parts for motor vehicles. The leading foundry states have traditionally been in the Great Lakes region; however, the industry is declining rapidly in the United States as foundry operations move to countries with lower labor costs. According to the American Foundry Society, in 2004 there were approximately 2,400 foundries, down from more than 6,000 fifty years earlier. There are several ways to cast metal. The most popular method is sand molding. Workers using this method pack a special sand around a pattern in a box called a flask. The flask is usually made in two parts—one for each half of the finished product. The pattern is removed, and molten metal is poured into the hollow made by the pattern in the sand. The hardened metal is removed once it has cooled. If the product is made in two parts, they are joined together using special pins and bushings. Other methods of casting use metal or ceramic molds or shells made of sand and resin. Sometimes metal is cast using dies or by spinning it at high speeds. Several kinds of foundry workers are involved in the casting process. Once a casting has been designed and a blueprint has been drawn up, highly skilled patternmakers prepare a wood or metal pattern in the exact shape of the casting. Most patternmakers prepare metal patterns using a variety of hand tools and metalworking machines. A few patterns are still made from wood. Wood patternmakers use hand and machine tools, glue, screws, and nails. Next, sand mixers prepare special sand, which pattern molders pack around the pattern to make a mold. Machine molders or hand molders pack the sand. Bench molders are hand molders who make molds for small castings. Floor molders are hand molders who make molds for large, bulky castings. Molders form the largest group of workers in the foundry industry. Coremakers fill patterns with sand to make cores. Cores are solid forms that shape the hollow inside metal castings. Like molders, coremakers work either by hand or with machinery. Coremakers who work by hand may be known as bench coremakers or floor coremakers, depending on the size of the cores that they make. More and more cores are being made by machine. Operators of these machines are known as machine coremakers. Most cores are baked in ovens by core oven tenders. Baking hardens and strengthens the sand cores. The cores are then placed in molds by the molders or by workers called core setters. Furnace operators control furnaces that heat and melt the metal that is to be cast. Pourers regulate the flow of the metal into the sand molds.

You should paint your shed if you have limited or no lighting inside it. Paint the interior a light color or white. It brightens the interior,...
Read More »
If it will serve as a garden shed, you will want it near your garden and within a reasonable distance of a water source. If it will primarily be...
Read More »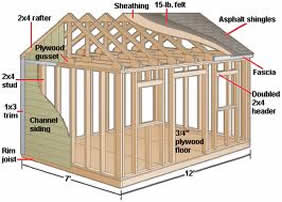
Once the metal has cooled into solid castings, shakeout workers take the castings out of the sand. The rough castings are sent to the cleaning and finishing department. Workers use several different processes to clean and smooth the castings. Shot blasters, or shot blast equipment operators, run machines that blast large castings with a mixture of air and metal shot or grit. Tumbler operators place smaller castings in revolving barrels with sand or a similar rough material. Chippers and grinders use hand tools and power chisels, files, and saws to remove excess metal and finish the castings. Many castings are also heat-treated to give them strength. Workers known as heat treaters, or annealers, run the furnaces in which the castings are heated. Finally, the castings are checked by casting inspectors, who make sure they meet the foundry's standards. Sometimes inspectors x-ray the metal castings to check for defects. Foundries employ many other workers including machinists, maintenance mechanics, millwrights, crane operators, and machine tool operators. In addition, foundries employ unskilled laborers, building custodians, office workers, and administrators. Professional and technical workers employed in foundries include engineers, metallurgists, and metallurgical technicians.

Balsa It's common knowledge, but Balsa is indeed the softest and lightest of all commercial woods. Nothing else even comes close. Useful for...
Read More »
Ultimately, the housing market is on its way back to normal, and that means lumber prices are likely to remain back in the normal trading range...
Read More »The best way to get a job in the foundry industry is by applying directly to foundries or to manufacturing plants that have their own foundries. You can contact local unions or foundries for information about getting into an apprenticeship program. Your state employment office may be able to help you find a job. Sometimes foundries place want ads in newspapers. If you attend an engineering or trade school, the school may be able to give you information about getting a job in a foundry. Workers in the foundry industry can advance within their trade, sometimes becoming supervisors of other workers; however, the employment outlook for foundry workers is poor through 2014. Even though a growing demand for metal castings is expected, the number of workers needed is anticipated to be reduced by more efficient production methods and the outsourcing of work to other countries. Openings for patternmakers, hand molders, and hand coremakers should occur primarily to replace workers who leave the field.

It's not recommended to place a tarp directly on your bike because it can work like a green house, accumulating heat and moisture. Heat can affect...
Read More »
Well, a potting shed is easier to keep warm throughout the year. The wooden sides and solid roof keep temperatures higher, protecting your young,...
Read More »

But to clean up goat poop, simply rake up the dung and any bedding material that's been soiled. Then, dispose of it. As long as our goats appear...
Read More »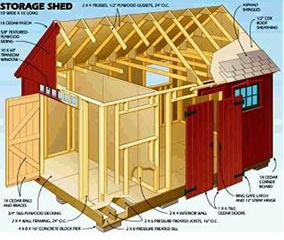
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
Mixing white and blue together creates light blue , also commonly known as sky blue. That's because any color mixed with white creates what's...
Read More »