 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Meruyert Gonullu
Photo: Meruyert Gonullu
Lumber Grade Lumber graded as #2 is the most common choice for floor joists and other framing lumber. It has more knots and defects than higher grades, but usually not enough to cause significant loss of bending strength.

5 = 72.5 pounds per cubic foot or 72.5 pounds per cubic meter. A 6-inch thick slab weighs 72.5 pounds per square foot, the maximum allowable...
Read More »
Real Wool, Mineral Wool, and Fiberglass Blown-In Mineral wool and real wool blown-in are less common but are healthier choices. Apr 5, 2021
Read More »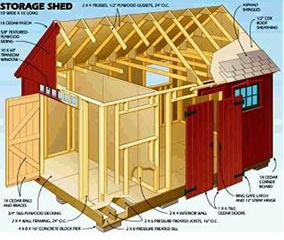
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »There are a number of factors to consider when framing a floor for a home building project, including:

There are three surefire ways to waterproof your wood for years to come. Use linseed or Tung oil to create a beautiful and protective hand-rubbed...
Read More »
Step 1 : Folding That is the most efficient way to use vacuum bag! This flattens the bag, allowing it to take up much less space in your suitcase....
Read More »
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »The amount of weight on the floor is also an important factor in determining joist size and span length. The weight of the building materials (joists, subfloor, flooring, and ceiling) is known as the dead load and is commonly rated at 10 pounds per square foot. You can calculate the dead weight yourself by adding up the weight of the building materials, then dividing by the number of square feet the materials will cover. The weight that will be placed on the floor is the live load and includes furnishing, people, and anything else you plan to store on the floor. Live loads range from 30 pounds per square foot and up, with 40 pounds the norm for most residential rooms and decks. Obviously if you’re a piano collector or plan to crowd as many people as possible onto your deck, you should err on the side of caution and increase the size of the floor joists or reduce the span.

Hard Metals – Since rats can't chew through hard metals like steel, it's one of the reasons it's recommended that holes are filled with wire mesh...
Read More »
Carport Canopy Planning Limitations A carport or canopy can not be built on land forward of a wall forming the principal elevation. Carports and...
Read More »
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
Plywood will absorb moisture quicker than OSB, but consequently it will also dry quicker. Both products will swell when wet, but plywood will...
Read More »
Your framing lumber and the oriented strand board (OSB) are going to be fine. The glues used to make OSB are water-resistant because the...
Read More »