 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Nataliya Vaitkevich
Photo: Nataliya Vaitkevich
Building Regulations would require at least 70 mm of high-performance foam insulation, or 150 mm of mineral wool, (although this will vary depending on floor type, construction, shape and size).

Top 10 Best Guitarists of All Time Rank Guitarist Top Strength 1 Guthrie Govan All-Around Technical Virtuoso 2 Pat Metheny Jazz Voicing & Picking 3...
Read More »
Standard Interior Door Height Code generally requires interior standard door sizes to have a certain height. It needs to be a minimum of 80 inches...
Read More »
There are many advantages to building a barndominium in Missouri. One of the most important advantages is the fact that they are much cheaper to...
Read More »
The Different Types of Home and Portable Wheelchair Ramps Threshold Ramps. A threshold ramp can be composed of either metal or rubber. ... Lego-...
Read More »
What size lumber for a 16 foot span:- as per general thumb rule and guidelines, for a 16 foot span, you will need atleast 2×10 size of lumber/...
Read More »
Create an Addition. Redo Your Kitchen. Renovate a Bathroom. Update Your Home's HVAC. Amplify Outdoor Living Space. Make Your Home More Accessible....
Read More »

First, the garage may be full of carbon monoxide from the car. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a real risk so it's important to make sure the garage...
Read More »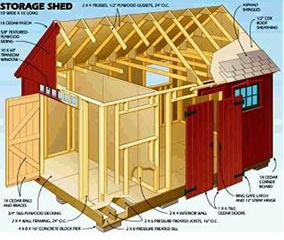
These are! They guide you every step of the way to complete your dream shed.
Learn More »
Yes, building one will require planning and working with a contractor, but the investment is worth it. But does a dropped kerb add more value? It...
Read More »