 DIY Builds
DIY Builds
 DIY Builds
DIY Builds

 Photo: Ellie Burgin
Photo: Ellie Burgin
"Ancient" is the key word in these Roman structures, which took a long, long time to develop their strength from seawater. Young cement built using a Roman recipe would probably not have the compressive strength to handle modern use — at least not initially.

It's simple – sheds don't typically need consents Typically, minor dwellings such as sheds are far less complex than a larger building and pose...
Read More »
One of the easiest and least expensive options for warming greenhouses in the winter is to create a thermal mass or heat sink. These are objects...
Read More »" " A chemical reaction within ancient Roman concrete actually makes the substance stronger over time, researchers have discerned. J. P. Oleson Why are millennia-old ancient Roman piers still standing strong as veritable concrete islands, while modern concrete structures built only decades ago crumble from an onslaught of wind and waves? The answer lies in an until-now undocumented Roman recipe. Researchers at the University of Utah discovered that as seawater filters through piers and breakwaters made of age-old Roman concrete, the structures actually become increasingly stronger because of the growth of interlocking minerals — including some minerals that are rare or expensive to cultivate in lab settings. " " This microscopic image shows the blocky calcium-aluminum-silicate-hydrate (C-A-S-H) binder material that forms when volcanic ash, lime, and seawater mix. Platy crystals of Al-tobermorite have grown among the C-A-S-H cementing matrix. Marie Jackson The study, published in the journal American Mineralogist, found that as seawater percolates through the concrete in the piers and breakwaters, it dissolves parts of the volcanic ash that was used in construction. This allows new minerals like Al-tobermorite and phillipsite to grow from the leached fluids. These minerals, similar in shape to the crystals in volcanic rocks, then formed interlocking plates in gaps within the ancient concrete, making the concrete stronger over time. This is pretty much the opposite of what happens to modern concrete structures, which are worn down by the elements and become increasingly cracked and brittle as pores and gaps are compromised by infiltrating seawater. So why aren't we using Roman-style concrete? For one, we don't know the recipe. We may think we're at the height of human knowledge, but the ancients did possess precious knowledge that has been lost to time. Although University of Utah geologist and lead study author Marie Jackson has pored through ancient Roman texts, she hasn't yet discovered a precise method for mixing the marine mortar. "The recipe was completely lost," said Jackson, who is working with geological engineers to recreate the right mix, in a press release. " " Ancient Romans made concrete by mixing volcanic ash with lime and seawater to make a mortar, and then incorporating into that mortar chunks of volcanic rock. The concrete was used inland as well, as in structures like the Pantheon in Rome. Stuart Black/robertharding/Getty Images There's also a load-bearing issue. "Ancient" is the key word in these Roman structures, which took a long, long time to develop their strength from seawater. Young cement built using a Roman recipe would probably not have the compressive strength to handle modern use — at least not initially. But that doesn't mean concocting a concrete mix using Roman engineering savvy wouldn't be useful. The concrete could potentially be used to replace other corrodible building materials — like steel and modern concrete — in newly constructed tidal lagoons, for instance, and other sea or sea-adjacent structures. Now That's Interesting What's the difference between concrete and cement? Concrete is a mixture of cement — a mineral powder — and water that is formed into a paste, then mixed with sand and rocks.

Metal buildings are extremely versatile. People use them for everything from carports and garages to outdoor workshops or private offices. Some...
Read More »
25 years Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic or PV panels, are made to last more than 25 years. In fact, many solar panels installed as early...
Read More »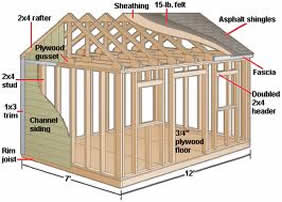

Today a typical cord of wood is cut to 16"" lengths of wood. So a half cord is made up of 3 rows of sixteen in pieces of wood to make it 4' deep. A...
Read More »
Number of cement bags are required for 100 sqft 6 inch slab = 11.4 bags.
Read More »

Embedded or concrete-in ground anchors are inherently stronger than those which are attached by bolts or screws. This makes them the most popular...
Read More »
Larger overhangs can help to keep you dry while standing at the shed's doorway and prevent the sun from heating your shed. Overhangs can vary from...
Read More »